Algorithms, Part I - Week 4 - 8 Puzzle
来自 Coursera 上普林斯顿大学的 Algorithms, Part I 课程的第四周编程作业8 Puzzle
分析
1 3 1 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
4 2 5 => 4 2 5 => 4 5 => 4 5 => 4 5 6
7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8
initial 1 left 2 up 5 left goal
A星算法
这次较难,大部分非关键代码通过CheckList能够解决,但是A* 算法课件里只有部分演示没有细讲,花了大把时间看A* 算法,发现一篇好文,最后核心代码是复制来的
总之,A* 结合了 Dijkstra’s(最短路径)和 Best-First-Search(自我探索)的优点
优先函数
A* 算法的实现需要依靠优先队列以及优先函数,题目介绍两种优先函数
Hamming(汉明)
Manhattan(曼哈顿)
8 1 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4 2 4 5 6 ———————- ———————-
7 6 5 7 8 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 2 2 0 3initial goal Hamming = 5 + 0 Manhattan = 10 + 0
汉明就是将不在目标位置的元素记为1,曼哈顿则是记录各个元素到目标位置的(水平垂直)距离和
游戏树
依照初始数据生成孪生结点
1 3 3 1 1 3 1 3 1 3 6 3
4 2 5 4 2 5 2 4 5 4 5 2 4 2 5 4 2 5
7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 8 7 6 7 8 1
board twin twin twin twin twin
一次使用一个孪生结点计算有效的邻居结点
8 1 3 8 1 3 8 1 8 1 3 8 1 3
4 2 4 2 4 2 3 4 2 4 2 5
7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6
previous search node neighbor neighbor neighbor
(disallow)
树根是初始数据,叶节点是邻居结点,叶节点保持在优先级队列中;在每个步骤中,A*算法从优先级队列中删除具有最小优先级的节点并将其子项添加到游戏树和优先级队列中
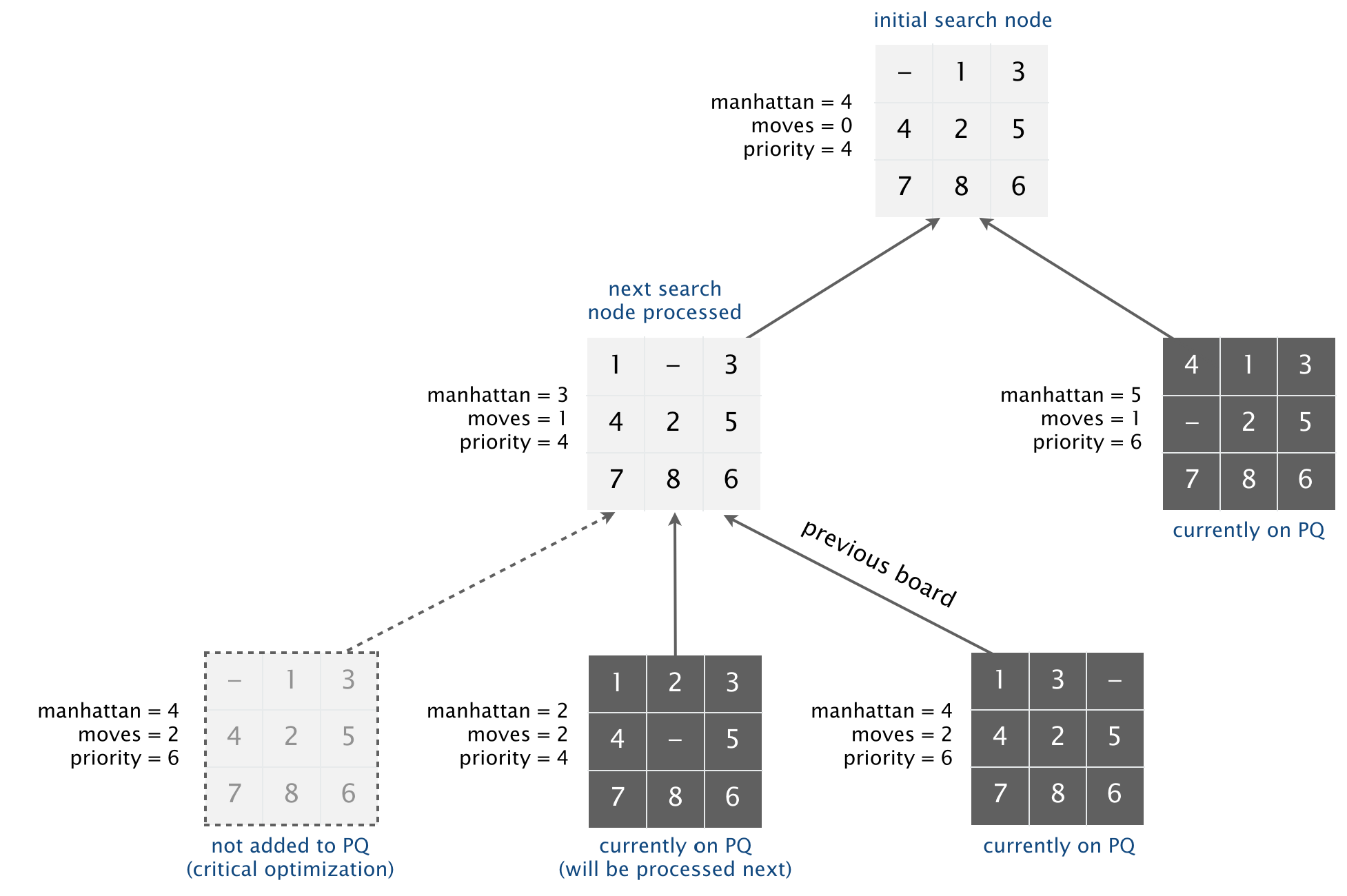
答案
Board.java
public class Board {
private final int[][] blocks;
private final int N;
// construct a board from an n-by-n array of blocks
// (where blocks[i][j] = block in row i, column j)
public Board(int[][] blocks) {
N = blocks.length;
this.blocks = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
this.blocks[i][j] = blocks[i][j];
}
// board dimension n
public int dimension() {
return N;
}
// number of blocks out of place
public int hamming() {
int hammingDis = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (isSpace(blocks[i][j])) continue;
if (blocks[i][j] != i * N + j + 1) hammingDis++;
}
}
return hammingDis;
}
// sum of Manhattan distances between blocks and goal
public int manhattan() {
int manhattanDis = 0;
int[] location = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (isSpace(blocks[i][j]))
continue;
if (blocks[i][j] != i * N + j + 1) {
location = findGoalLocation(blocks[i][j]);
manhattanDis += Math.abs(i - location[0]) + Math.abs(j - location[1]);
}
}
}
return manhattanDis;
}
private int[] findGoalLocation(int data) {
int[] ij = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
if (data == N * i + j + 1)
{ ij[0] = i; ij[1] = j; }
return ij;
}
// is this board the goal board?
public boolean isGoal() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (blocks[i][j] == 0) continue;
if (blocks[i][j] != i * N + j + 1) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// a board that is obtained by exchanging any pair of blocks
public Board twin() {
for (int row = 0; row < blocks.length; row++)
for (int col = 0; col < blocks.length - 1; col++)
if (!isSpace(blocks[row][col]) && !isSpace(blocks[row][col + 1]))
return new Board(swap(row, col, row, col + 1));
throw new RuntimeException();
}
// does this board equal y?
public boolean equals(Object y) {
if (y == null) return false;
if (y.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
if (y == this) return true;
Board that = (Board) y;
if (this.dimension() != that.dimension()) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < this.dimension(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < this.dimension(); j++) {
if (this.blocks[i][j] != that.blocks[i][j])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// all neighboring boards
public Iterable<Board> neighbors() {
Queue<Board> neighbors = new Queue<Board>();
int[] location = spaceLocation();
int spaceRow = location[0];
int spaceCol = location[1];
if (spaceRow > 0) neighbors.enqueue(new Board(swap(spaceRow, spaceCol, spaceRow - 1, spaceCol)));
if (spaceRow < dimension() - 1) neighbors.enqueue(new Board(swap(spaceRow, spaceCol, spaceRow + 1, spaceCol)));
if (spaceCol > 0) neighbors.enqueue(new Board(swap(spaceRow, spaceCol, spaceRow, spaceCol - 1)));
if (spaceCol < dimension() - 1) neighbors.enqueue(new Board(swap(spaceRow, spaceCol, spaceRow, spaceCol + 1)));
return neighbors;
}
private int[][] swap(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int[][] copy = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
copy[i][j] = blocks[i][j];
int tmp = copy[row1][col1];
copy[row1][col1] = copy[row2][col2];
copy[row2][col2] = tmp;
return copy;
}
private int[] spaceLocation() {
for (int row = 0; row < blocks.length; row++)
for (int col = 0; col < blocks.length; col++)
if (isSpace(blocks[row][col])) {
int[] location = new int[2];
location[0] = row;
location[1] = col;
return location;
}
throw new RuntimeException();
}
private boolean isSpace(int block) {
return block == 0;
}
// string representation of this board (in the output format specified below)
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append(N + "\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
s.append(String.format("%2d ", blocks[i][j]));
}
s.append("\n");
}
return s.toString();
}
// unit tests (not graded)
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}Solver.java
public class Solver {
private MinPQ<SearchNode> pq;
private Stack<Board> solutions;
private int Moves = -1;
private boolean solved;
private class SearchNode implements Comparable<SearchNode>{
private final Board board;
private final int move;
private final int priority;
private final SearchNode parent;
private final boolean isTwin;
public SearchNode(Board board, int move, SearchNode parent, boolean isTwin){
this.board = board;
this.move = move;
this.priority = board.manhattan() + move;
this.parent = parent;
this.isTwin = isTwin;
}
public int compareTo(SearchNode that) {
if (this.board.equals(that.board)) return 0;
if (this.priority < that.priority) return -1;
else return 1;
}
}
// find a solution to the initial board (using the A* algorithm)
public Solver(Board initial) {
if (initial == null)
throw new java.lang.NullPointerException();
Board initialTwin = initial.twin();
pq = new MinPQ<SearchNode>();
solutions = new Stack<Board>();
SearchNode initialNode = new SearchNode(initial, 0, null, false);
SearchNode twinNode = new SearchNode(initialTwin, 0, null, true);
pq.insert(initialNode);
pq.insert(twinNode);
while(true){
//solve for original
SearchNode searchNode = pq.delMin();
if (searchNode.board.isGoal()) {
if (!searchNode.isTwin) {
this.solved = true;
Moves = searchNode.move;
this.solutions.push(searchNode.board);
while(searchNode.parent != null){
searchNode = searchNode.parent;
this.solutions.push(searchNode.board);
}
}
break;
}
else {
for (Board neiborBoard: searchNode.board.neighbors()){
SearchNode neiborNode = new SearchNode(neiborBoard, searchNode.move+1, searchNode, searchNode.isTwin);
if (searchNode.parent == null){
pq.insert(neiborNode);
} else if (!searchNode.parent.board.equals(neiborNode.board)){
pq.insert(neiborNode);
}
}
}
}
}
// private reconstructPath()
// is the initial board solvable?
public boolean isSolvable() {
return solved;
}
// min number of moves to solve initial board; -1 if unsolvable
public int moves() {
// return solutions.size();
return Moves;
}
// sequence of boards in a shortest solution; null if unsolvable
public Iterable<Board> solution() {
if (isSolvable())
return solutions;
else
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create initial board from file
In in = new In(args[0]);
int n = in.readInt();
int[][] blocks = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
blocks[i][j] = in.readInt();
Board initial = new Board(blocks);
// solve the puzzle
Solver solver = new Solver(initial);
// print solution to standard output
if (!solver.isSolvable())
StdOut.println("No solution possible");
else {
StdOut.println("Minimum number of moves = " + solver.moves());
for (Board board : solver.solution())
StdOut.println(board);
}
}
}