Algorithms, Part I - Week 3 - Pattern Recognition
来自 Coursera 上普林斯顿大学的 Algorithms, Part I 课程的第三周编程作业Pattern Recognition
分析
题目大意:在一平面内给定 n 个随机点,找出可以连接4点及以上的最长直线段

问题就是识别模型是否有4点及以上共线
Point 数据类型
public class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
public Point(int x, int y) // constructs the point (x, y)
public void draw() // draws this point
public void drawTo(Point that) // draws the line segment from this point to that point
public String toString() // string representation
public int compareTo(Point that) // compare two points by y-coordinates, breaking ties by x-coordinates
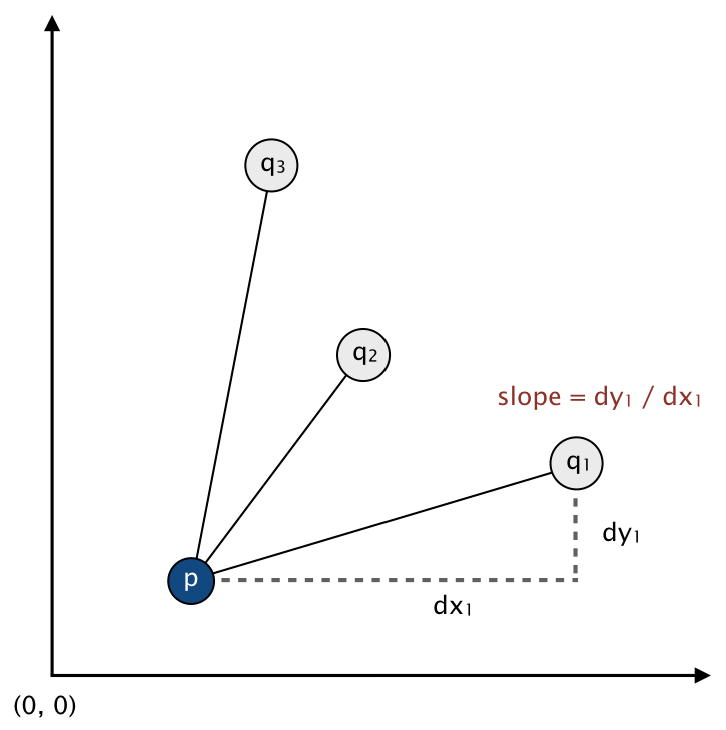
public double slopeTo(Point that) // the slope between this point and that point
public Comparator<Point> slopeOrder() // compare two points by slopes they make with this point
}课件给了一个半成品,相对容易能够完成
这里说一下 slopeOrder() 的实现
实现方法在 checklists 里有解答,就是实现 Comparator 接口
To do this, create a private nested (non-static) class SlopeOrder that implements the Comparator<Point> interface. This class has a single method compare(q1, q2) that compares the slopes that q1 and q2 make with the invoking object p. the slopeOrder() method should create an instance of this nested class and return it.
创建一个叫 SlopeOrder 的私有内部类,并实现 Comparator 接口。在这个类里创建一个 compare(q1, q2) 方法, 然后在 slopeOrder() 中创建一个 SlopeOrder 的实例并返回。
public Comparator<Point> slopeOrder() {
return new SlopeOrder();
}
private class SlopeOrder implements Comparator<Point> {
public int compare(Point q1, Point q2) {
}
}暴力算法
不做任何算法优化的方法,同样 checklists 也给出步骤
一次检查4点, 检查它们是否全都位于同一线段上, 返回所有这些线段
要检查4点 p、q、r、s 是否共线, 就检查 p 和 q 之间,p 和 r 之间,p 和 s 之间这三个斜率是否相等即可
具体实现的时候犯了一个微小的致命错误,题目要求传进来的参数不能被改变,一想解决方法很简单就是复制出来使用
但用的是等号 copies = points; 直接赋值,这只是增加了一个关于 points 的引用,结果就是后面的 test 那个点过不去
正确方法就是用 for 循环赋值,这样一来在程序后面对 copies 进行排序时就不会连同改变传进来的 points 参数了
题目要求检查输入不能有重复的点,解决方法就是先按升序排序,然后遍历比较
排序用到 Arrays.sort() ,这时 之前在 Point 类中实现的 compareTo() 就起作用了
快速算法
一个以排序为基础的快速算法
官方给出的具体实现
- Think of p as the origin.
- For each other point q, determine the slope it makes with p.
- Sort the points according to the slopes they makes with p.
- Check if any 3 (or more) adjacent points in the sorted order have equal slopes with respect to p. If so, these points, together with p, are collinear.
意思就是一次取一个参照点 p,求与其它点的斜率,然后按照斜率来排序其它点,遍历比较当有3个或以上点的斜率相同时即可说明四点共线
答案
Point.java
public class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
private final int x; // x-coordinate of this point
private final int y; // y-coordinate of this point
public Point(int x, int y) {
/* DO NOT MODIFY */
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void draw() {
/* DO NOT MODIFY */
StdDraw.point(x, y);
}
public void drawTo(Point that) {
/* DO NOT MODIFY */
StdDraw.line(this.x, this.y, that.x, that.y);
}
public double slopeTo(Point that) {
/* YOUR CODE HERE */
if (this.y == that.y) { // horizontal
if (this.x == that.x) {
return Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
}
return 0.0;
}
if (this.x == that.x) // vertical
return Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
return (double)(that.y - this.y) / (that.x - this.x);
}
public int compareTo(Point that) {
/* YOUR CODE HERE */
if (this.y < that.y || (this.y == that.y && this.x < that.x))
return -1;
else if (this.y == that.y && this.x == that.x)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
public Comparator<Point> slopeOrder() {
/* YOUR CODE HERE */
return new SlopeOrder();
}
private class SlopeOrder implements Comparator<Point>
{
public int compare(Point q1, Point q2) {
double slope1 = Point.this.slopeTo(q1);
double slope2 = Point.this.slopeTo(q2);
if (slope1 > slope2) return 1;
if (slope1 < slope2) return -1;
return 0;
}
}
public String toString() {
/* DO NOT MODIFY */
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ")";
}
}BruteCollinearPoints.java
public class BruteCollinearPoints {
private Point[] copies;
private ArrayList<LineSegment> lineSegments = new ArrayList<LineSegment>();
// finds all line segments containing 4 points
public BruteCollinearPoints(final Point[] points) {
if (points == null)
throw new java.lang.NullPointerException();
copies = new Point[points.length];
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
copies[i] = points[i];
}
// sort by y-coordinate
// the endpoints are the first and last points
Arrays.sort(copies);
// after sort then can check if duplicate
for (int i = 0; i < copies.length - 1; i++)
if (copies[i].compareTo(copies[i+1]) == 0)
throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException();
for (int ip = 0; ip < copies.length-3; ip++) {
for (int iq = ip + 1; iq < copies.length-2; iq++) {
double slopeP2Q = copies[ip].slopeTo(copies[iq]);
for (int ir = iq + 1; ir < copies.length-1; ir++) {
double slopeQ2R = copies[iq].slopeTo(copies[ir]);
if (slopeP2Q != slopeQ2R) continue;
for (int is = ir + 1; is < copies.length; is++) {
double slopeR2S = copies[ir].slopeTo(copies[is]);
// if 3 of 4's slopes are equal then 4 points are colllinear
if (slopeP2Q == slopeR2S)
lineSegments.add(new LineSegment(copies[ip], copies[is]));
}
}
}
}
}
// the number of line segments
public int numberOfSegments() {
return lineSegments.size();
}
// the line segments
public LineSegment[] segments() {
LineSegment[] result = new LineSegment[lineSegments.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < lineSegments.size(); i++) {
result[i] = lineSegments.get(i);
}
return result;
}
}FastCollinearPoints.java
public class FastCollinearPoints {
private Point[] copies;
private ArrayList<LineSegment> lineSegments = new ArrayList<LineSegment>();
// finds all line segments containing 4 or more points
public FastCollinearPoints(Point[] points) {
if (points == null)
throw new java.lang.NullPointerException();
copies = new Point[points.length];
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
copies[i] = points[i];
}
// sort by y-coordinate
// the endpoints are the first and last points
Arrays.sort(copies);
// after sort then can check if duplicate
for (int i = 0; i < copies.length - 1; i++)
if (copies[i].compareTo(copies[i+1]) == 0)
throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException();
for (int i = 0; i < copies.length - 1; i++) {
Point origin = copies[i]; // Think of p as the origin.
double[] slopes = new double[copies.length - 1 - i];
Point[] others = new Point[copies.length - 1 - i];
for (int j = 0; j < copies.length - 1 - i; j++)
others[j] = copies[j + 1 + i];
// For each other point q, determine the slope it makes with p
for (int j = 0; j < others.length; j++)
slopes[j] = origin.slopeTo(others[j]);
// Sort the points according to the slopes they makes with p
Arrays.sort(others, origin.slopeOrder());
Arrays.sort(slopes);
// Check if any 3 (or more) adjacent points in the
// sorted order have equal slopes with respect to p
// If so, these points, together with p, are collinear
for (int cnt_same = 0, j = 0; j < slopes.length - 1; j++) {
if (slopes[j] == slopes[j+1]) {
cnt_same++;
}
if (cnt_same >= 2) {
lineSegments.add(new LineSegment(origin, others[j + 1]));
break;
}
}
}
}
// the number of line segments
public int numberOfSegments() {
return lineSegments.size();
}
// the line segments
public LineSegment[] segments() {
LineSegment[] result = new LineSegment[lineSegments.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < lineSegments.size(); i++) {
result[i] = lineSegments.get(i);
}
return result;
}
}